
Coaxial Cable
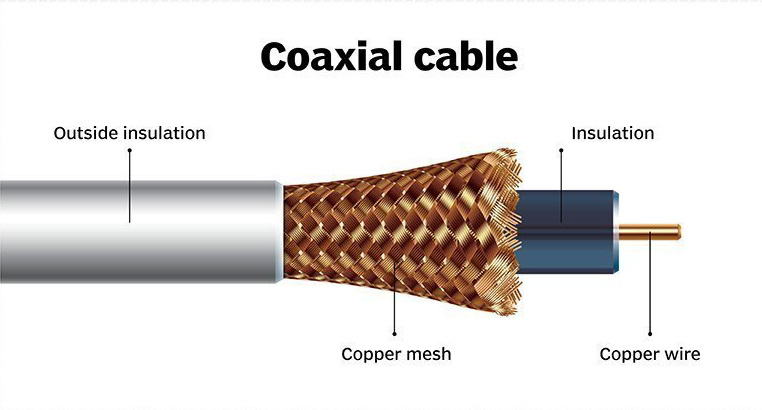
Coaxial cable is a type of electrical cable that has an inner conductor surrounded by a tubular insulating layer, surrounded by a tubular conducting shield.
Implementation Standards
- BT Specifications
Product Introduction
Applications
Coaxial cable is used as a transmission line for radio frequency signals. Its applications include feedlines connecting radio transmitters and receivers with their antennas, computer network (Internet) connections, digital audio (S/PDIF), and distributing cable television signals.
Description of Coaxial Cable
Coaxial cable conducts electrical signal using an inner conductor (usually a solid copper, stranded copper or copper plated steel wire) surrounded by an insulating layer and all enclosed by a shield, typically one to four layers of woven metallic braid and metallic tape. The cable is protected by an outer insulating jacket.
Technical Characteristics
- Characteristic Impedance: Determined by the dielectric constant of the inner insulator and the radii of the inner and outer conductors.
- Attenuation: Varies as a function of frequency.
- Voltage Handling: Capability depends on construction.
- Shield Quality: Affects signal protection from external interference.
Common Applications
- Video and CATV distribution
- RF and microwave transmission
- Computer and instrumentation data connections
Technical Specifications
Coaxial Cable Specifications
| Item | Specifications |
| Conductor | Solid copper or Tinned Copper |
| Insulation | PE |
| Shield | Tinned copper or Bonded aluminium polyethylene terephthalate |
| Screen | Tinned copper |
| Outersheath | Flame-retardant-polyvinyl chloride (FR-PVC) or Low Smoke Zero Halogen (LSZH) |
Application Fields
Radio frequency signal transmission
Computer network connections
Digital audio (S/PDIF)
Cable television signal distribution
Professional TV and CCTV system installations
Packaging & Shipping
All cables will be packaged in different materials based on their outer diameter and net weight, and can be customized according to requirements
